How Many Hearts Do Turtles Have?
Turtles are fascinating creatures that have been around for millions of years. They have unique characteristics that make them stand out from other animals, such as their hard shells and slow movement. One question that many people have about turtles is how many hearts they have.
While most animals have only one heart, turtles are a bit different. In fact, turtles have a unique circulatory system that involves not one, not two, but three separate hearts! This may seem strange, but it actually makes sense for these unique creatures. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the fascinating world of turtle biology and explore the secrets of their multiple hearts.
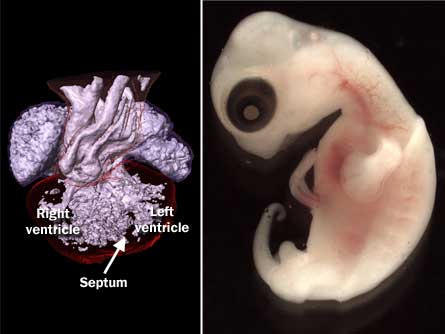
How Many Hearts Do Turtles Have?
Turtles are fascinating creatures with unique characteristics that have long fascinated scientists and animal lovers alike. One of the most interesting aspects of turtles is their circulatory system, specifically the number of hearts they possess. In this article, we will explore the question of how many hearts turtles have, diving into the science behind this remarkable feature.
What is the Basic Anatomy of a Turtle?
The anatomy of a turtle is quite distinct from most other animals. Turtles are reptiles, which means they are cold-blooded and have a scaly skin. They have a hard shell that covers their body and provides them with protection from predators. Turtles have a beak-like mouth that they use to bite and tear food, and they have four legs with webbed feet that they use to swim.
The Circulatory System of Turtles
The circulatory system of turtles is an essential aspect of their anatomy. It is responsible for the transport of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout their body. The heart of a turtle is a muscular organ that pumps blood through their circulatory system. Turtles have a closed circulatory system, which means that their blood is contained within vessels.
How Many Hearts Do Turtles Have?
Turtles have a unique circulatory system that includes two hearts. The first heart is the systemic heart, which pumps oxygenated blood to the body. The second heart is the pulmonary heart, which pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs. This system allows turtles to efficiently extract oxygen from the air they breathe and distribute it throughout their body.
Benefits of Having Two Hearts
Having two hearts provides turtles with several benefits. Since turtles are cold-blooded, they rely on external heat sources to regulate their body temperature. The division of labor between the two hearts allows turtles to divert more blood to their lungs when they need to warm up quickly. This helps them to increase their metabolic rate and generate heat more efficiently.
How Do Turtles Keep Their Hearts Healthy?
Just like humans, turtles need to keep their hearts healthy to live a long and healthy life. Turtles in the wild get their exercise by swimming and foraging for food. This helps to keep their heart muscles strong and healthy. In captivity, it is essential to provide turtles with enough space to move around and access to a varied diet to ensure their heart health.
VS: Turtles in Captivity
Turtles in captivity are susceptible to various health problems, including heart disease. One of the main reasons for this is the lack of exercise and a limited diet. Turtles need plenty of space to move around and access to a varied diet to keep their hearts healthy. It is essential to provide turtles in captivity with a suitable environment that meets their physical and dietary needs.
The Role of a Vet in Keeping Turtles Healthy
A veterinarian can play a crucial role in keeping turtles healthy. Regular check-ups can help to identify any potential health problems early on and prevent them from becoming more severe. A vet can also provide advice on the best diet and exercise regimen for a turtle to keep their heart healthy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, turtles have two hearts – the systemic heart and the pulmonary heart. Having two hearts provides turtles with several benefits, including better heat regulation and more efficient oxygen distribution. To keep their hearts healthy, turtles need plenty of exercise and a varied diet. By providing turtles with a suitable environment and access to veterinary care, we can help to ensure they live happy and healthy lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about turtles and their anatomy.
What is the anatomy of a turtle?
Turtles have a unique anatomy that sets them apart from other animals. They have a shell made of bone and cartilage that protects their body. They also have a beak-like mouth and four legs that are adapted for swimming or walking on land.
Additionally, turtles have a unique respiratory system that allows them to remain underwater for extended periods. They have two sets of lungs and can extract oxygen from the water through specialized glands in their mouth and throat.
Do turtles have a heart?
Yes, turtles do have a heart. Like other vertebrates, turtles have a four-chambered heart that pumps blood throughout their body. The heart is located in the chest cavity, just below the lungs.
However, unlike most other animals, turtles have a slow heart rate. Their heart rate can range from 10 to 35 beats per minute, depending on their activity level and environmental conditions.
How many hearts do turtles have?
Turtles have only one heart, which is located in the chest cavity. Despite their unique anatomy and physiology, turtles do not have multiple hearts.
However, some species of turtles have a modified circulatory system that allows them to divert blood away from their lungs when they are underwater. This allows them to conserve oxygen and stay submerged for longer periods of time.
What is the role of a turtle’s heart?
The heart of a turtle plays a critical role in maintaining the animal’s overall health and wellbeing. It pumps oxygen-rich blood to the turtle’s muscles and organs, allowing them to function properly.
The heart also helps to regulate the turtle’s body temperature and metabolism. When a turtle is cold, its heart rate slows down, which reduces its energy needs. Conversely, when a turtle is warm, its heart rate increases, which helps to maintain its body temperature and metabolic rate.
How does a turtle’s heart rate compare to other animals?
Turtles have a slow heart rate compared to many other animals. Their heart rate can range from 10 to 35 beats per minute, depending on their activity level and environmental conditions.
By contrast, the average heart rate for humans is approximately 60 to 100 beats per minute, while the average heart rate for a dog is around 60 to 140 beats per minute, depending on the breed.
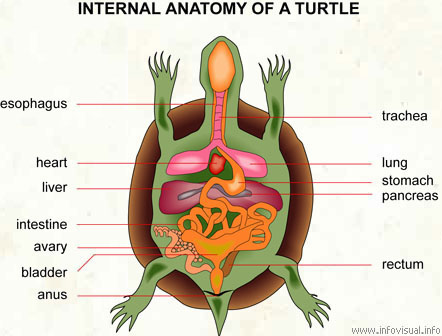
Exposed Heart Turtle Flaps Her Arms Whenever Her Dad Comes Near Her Tank | The Dodo Faith = Restored
In conclusion, turtles are fascinating creatures that have been around for millions of years. They are known for their hard shells and slow movements, but did you know that they also have unique anatomy? One interesting fact is that turtles have multiple hearts, with the exact number varying between species.
While most turtles have three hearts, some species can have up to four. These additional hearts are located near the turtles’ necks and help to circulate blood to their heads and extremities. This adaptation allows turtles to regulate their body temperature and remain active in colder environments.
Overall, the number of hearts turtles have is just one of the many fascinating aspects of these ancient creatures. From their unique shells to their impressive lifespans, turtles continue to capture our imaginations and inspire us to learn more about the world around us.

